Consult For
Diagnostic & General Medical Services
Diagnostic & General Medical Services
- Comprehensive Medical Assessment
- Evaluation of symptoms and conditions affecting multiple organ systems
- Diagnosis of complex and undifferentiated medical issues
- Chronic Disease Management
- Hypertension, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and lipid abnormalities
- Autoimmune diseases, chronic liver, kidney, or heart conditions
- Preventive Care
- Regular health check-ups, screening for lifestyle-related diseases
- Vaccination programs for adults and at-risk individuals
Acute Medical Care
Acute Medical Care
Multisystem Disease Management
Multisystem Disease Management
Critical Care Management
Critical Care Management
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Management
- Monitoring and management of critically ill patients with multi-organ failure
- Use of advanced monitoring devices, ventilators, and dialysis machines
- Emergency Resuscitation
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), management of shock, and acute trauma care
- Ventilator Management
- Non-invasive and invasive mechanical ventilation
- Weaning protocols for patients recovering from respiratory failure
- Hemodynamic Monitoring and Support
- Management of unstable blood pressure and circulation using inotropes and vasopressors
Infectious Disease Management
Infectious Disease Management
Post-ICU Rehabilitation
Post-ICU Rehabilitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), management of shock, and acute trauma care
CPR, shock management, and acute trauma care are critical services aimed at saving lives in emergencies. These interventions address life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest, severe shock, or trauma-related complications and require swift, coordinated actions.
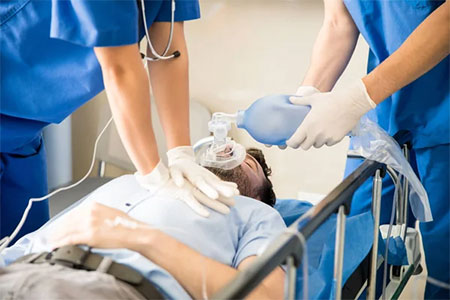
1. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
Purpose: Restore blood circulation and oxygenation in cases of cardiac or respiratory arrest.
2. Management of Shock
Purpose: Stabilize blood flow and oxygen delivery to vital organs in cases of systemic circulatory failure.
3. Acute Trauma Care
Purpose: Manage life-threatening injuries and prevent secondary complications following accidents or physical trauma.
Role of the Specialist
- Coordination of Multidisciplinary Teams: Collaborating with surgeons, anesthetists, and emergency physicians for seamless care.
- Decision-Making in Critical Situations: Rapid assessment of the severity of shock or trauma. Prioritizing interventions based on life-threatening conditions.
- Post-Emergency Care: Monitoring recovery and addressing complications. Rehabilitation and follow-up care to restore health and functionality.
Benefits of Timely Intervention
- Survival Improvement: Quick action during cardiac arrest or shock increases chances of survival.
- Reduced Complications: Early stabilization minimizes long-term damage to organs.
- Enhanced Recovery: Comprehensive trauma care ensures better physical and psychological outcomes.
