Consult For
Diagnostic & General Medical Services
Diagnostic & General Medical Services
- Comprehensive Medical Assessment
- Evaluation of symptoms and conditions affecting multiple organ systems
- Diagnosis of complex and undifferentiated medical issues
- Chronic Disease Management
- Hypertension, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and lipid abnormalities
- Autoimmune diseases, chronic liver, kidney, or heart conditions
- Preventive Care
- Regular health check-ups, screening for lifestyle-related diseases
- Vaccination programs for adults and at-risk individuals
Acute Medical Care
Acute Medical Care
Multisystem Disease Management
Multisystem Disease Management
Critical Care Management
Critical Care Management
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Management
- Monitoring and management of critically ill patients with multi-organ failure
- Use of advanced monitoring devices, ventilators, and dialysis machines
- Emergency Resuscitation
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), management of shock, and acute trauma care
- Ventilator Management
- Non-invasive and invasive mechanical ventilation
- Weaning protocols for patients recovering from respiratory failure
- Hemodynamic Monitoring and Support
- Management of unstable blood pressure and circulation using inotropes and vasopressors
Infectious Disease Management
Infectious Disease Management
Post-ICU Rehabilitation
Post-ICU Rehabilitation
Non-invasive & invasive mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation supports or replaces natural breathing in patients with respiratory failure or compromised lung function. It is a critical intervention used to maintain adequate oxygenation and ventilation in acute and chronic conditions.
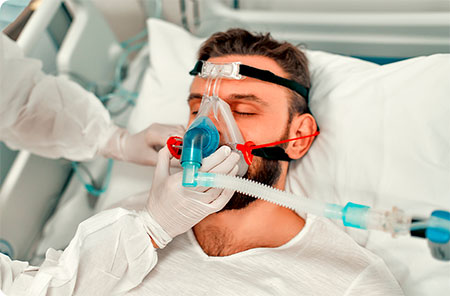
1. Non-Invasive Mechanical Ventilation (NIV)
Purpose: Provide respiratory support without inserting a tube into the airway.
Key Features
- Delivered via a mask (nasal, full-face, or helmet).
- Preserves natural airway reflexes and reduces the risk of infection.
Indications for NIV
- Respiratory distress due to COPD or asthma exacerbations.
- Acute pulmonary edema.
- Post-operative respiratory support.
- Preventing progression to invasive ventilation.
2. Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
Purpose: Provide complete control of breathing in critically ill patients by securing the airway with an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube.
Key Features
- Requires intubation (placement of a tube into the windpipe).
- Delivers precise oxygen concentrations, respiratory rates, and pressures.
Indications for Invasive Ventilation
- Severe respiratory failure or ARDS.
- Post-cardiac arrest care.
- Multi-organ failure requiring ICU support.
- Inability to protect the airway (e.g., in comatose patients).
- Failed NIV.
Common Conditions Requiring Ventilation
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
- Severe pneumonia or COVID-19-related respiratory failure.
- Neuromuscular disorders affecting respiratory muscles.
- Trauma or surgical complications.
Advantages of Mechanical Ventilation
- Maintains oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal.
- Prevents lung collapse in critical patients.
- Supports recovery while addressing the underlying condition.
Role of Specialists
- Manage respiratory conditions and determine the need for ventilation.
- Address complications like diabetic ketoacidosis causing respiratory failure.
- Treat infections like pneumonia or sepsis contributing to respiratory distress.
- Oversee ventilation settings, monitor response, and prevent complications.
